22 May Smart Farming in Durian Plantation Industry: A Complete Guide

With rapid developments in technology, our agricultural practices in durian planting have evolved greatly over the last few years – progressing from manual labor, to machines, to fully-automated processes.
Most notably, the introduction of smart farming in the 20th century has helped farmers to achieve higher levels of efficiency and precision in durian production, allowing them to minimize losses and maximize profits.
Therefore, this article will cover all the essentials of smart farming in the durian industry. We’ll guide you through the technologies, benefits, and challenges of implementing state of the art infrastructures.
What is the Meaning of Smart Farming?
Smart farming is the management of farms using intelligent information and communication technology systems to boost and optimize production systems.
These advanced systems include technologies such as sensors, Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and networking to the farming system.
Through this system, farmers can remotely monitor and tend to their crops with exceptional levels of accuracy.
Do note that due to the interconnected nature of this system, smart farming is only feasible in regions with access to smartphones and internet connectivity.
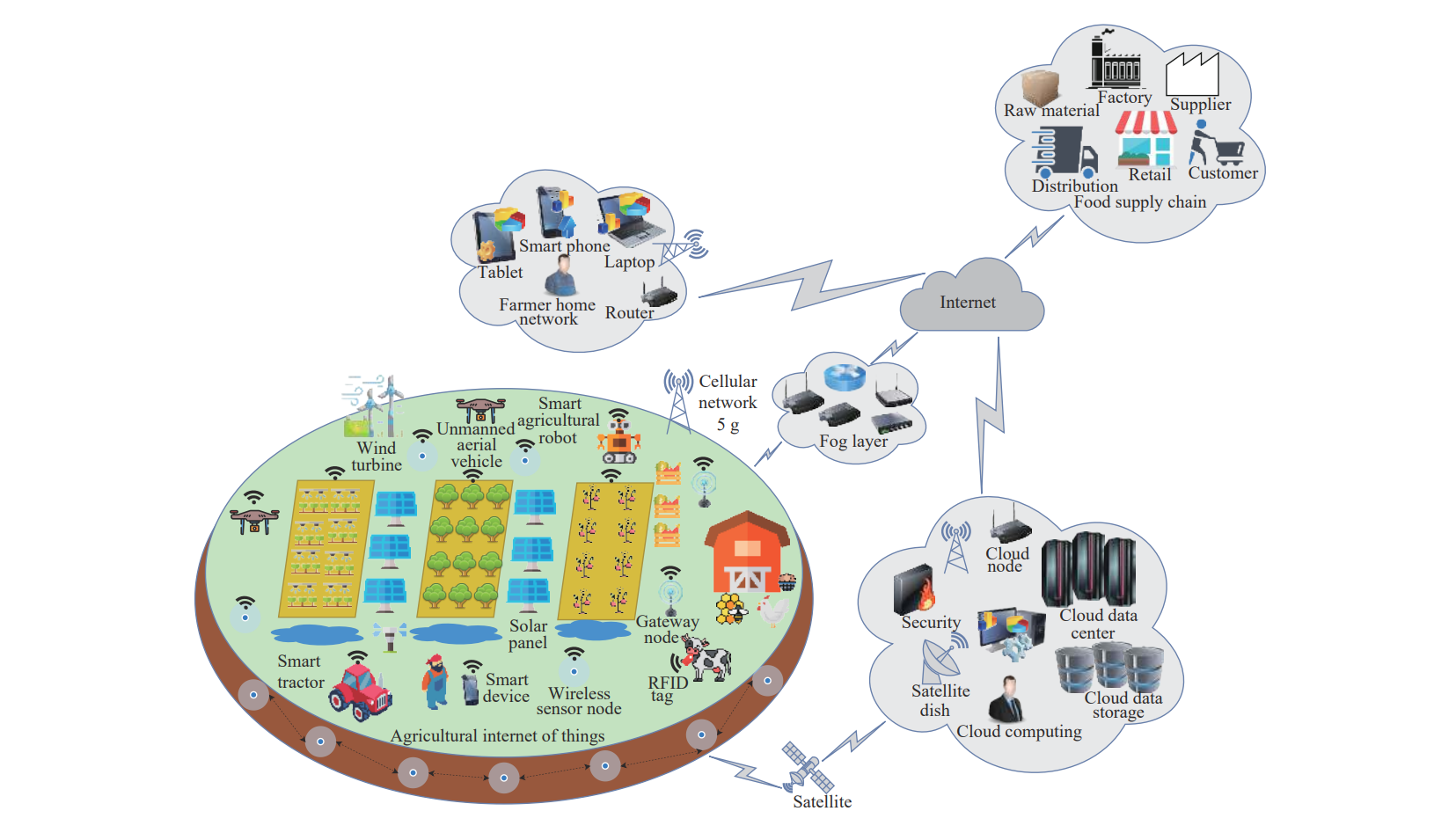
Example of a Smart Farm (Source: Friha et al., 2021).
According to Friha et al. (2021), there are five main layers in the smart farming system:
- Physical: The physical components of the smart farm which perform sensing and control actions (e.g., sensors, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), agricultural robots).
- Networking: Responsible for the transmission of data and commands collected by the physical layer.
- Middleware: Handles the complexity of hardware and software, simplifying the use and development of IoT applications and services.
- Service: Provides technologies such as cloud computing, fog computing, and AI for the application layer.
- Application: Uses the services provided by the previous layers and employs IoT-based messaging protocols to perform agricultural activities with minimal human interaction. (e.g., helps the farmer make decisions such as “when to fertilize the plants”).
Smart Farming in Durian Plantations
Smart farming has been credited for enabling better performance and reducing cost for durian plantations. Many durian farmers have opted to use technologies such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) or drones, and sensors.
UAVs aid in manual labor reduction, farm monitoring, and precise fertilization, while sensors help to measure factors such as temperature, humidity, mineral contents, and overall soil fertility – making them important assets in durian farming.
On the topic of the “adoption of durian smart farming technologies” a Thailand study found that the use of smart farming was affected by factors such as farmer’s age, farmer’s main occupation, access to extension services, and farm size.
The findings of this study revealed that:
- Younger farmers with larger farm sizes were more likely to adopt smart farming technologies, compared to older farmers with smaller farm sizes.
- Farmers whose primary occupation is farming, and who have access to extension services were more likely to adopt smart farming technologies, compared to those who do not.
Although the research was conducted in Thailand, it is clearly applicable in the Malaysian context: With access to extension services (agricultural support services), Malaysian durian farmers are more likely to adopt smart farming to increase production and profit.
This highlights the importance of providing sufficient resources and assistance to local farmers.
Curious about the potential of durian farming? Read this article on Why Durian Farming is Malaysia’s Next Big Investment.
What are Smart Farming Technologies?
In this section, we’ll be highlighting several smart farming technologies used in durian plantations:
1. Sensors
Sensors are devices that detect and measure changes in various aspects of the farm environment. These sensors allow farmers to understand the condition of their crops without being physically there.
Moreover, sensors are more accurate compared to traditional or manual methods of monitoring durian plantations. These devices are also able to detect issues (e.g., plant diseases) in the early stages.
This information helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, farm and disease management, and other management practices to ensure optimal crop health and yield.
Assisted by the smart system, the farmers can then take action remotely.
For instance, this IoT based smart irrigation management system uses sensors to detect soil moisture, soil temperature, air temperature, Ultraviolet (UV) light radiation, and more.
The system will then make automatic adjustments to the irrigation schedule, with the primary goal of achieving optimum and efficient use of water.
Overall, these sensors are able to collect valuable data, which can be stored away in the cloud and accessed at any time, as part of the IoT system structure. As discussed in this section, this data helps farmers to manage their plantations more efficiently.
2. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)
UAVs, also known as drones, are small aircrafts that are controlled remotely by one or two operators. These machines can also be semi or fully autonomous (operates by itself).
In durian plantations, UAVs are equipped with cameras, sensors, and GPS to collect data for applications such as mapping of weed and management, crops growth monitoring and yield estimation, and disease detection.
They can cover large areas quickly and provide farmers with valuable insights into their crops’ condition, helping them detect issues early and take immediate action.
Besides monitoring, UAVs can also be used for spraying liquids like fertilizer and pesticides. For instance, the model Agras MG-1-DJI is 70 times faster than manual spraying.
This UAV can carry 10 kg of liquid over an area of 4000 – 6000 square meters in the span of 10 mins. With this machine, farmers can reduce manual labor, thus saving costs and increasing efficiency on the farm.
A 2021 study provided a great summary of the the function of UAVs in agriculture, stating that UAVs have greatly assisted farmers through:
- Very accurate data capturing
- Faster spraying of farms
- Comprehensive monitoring of farms
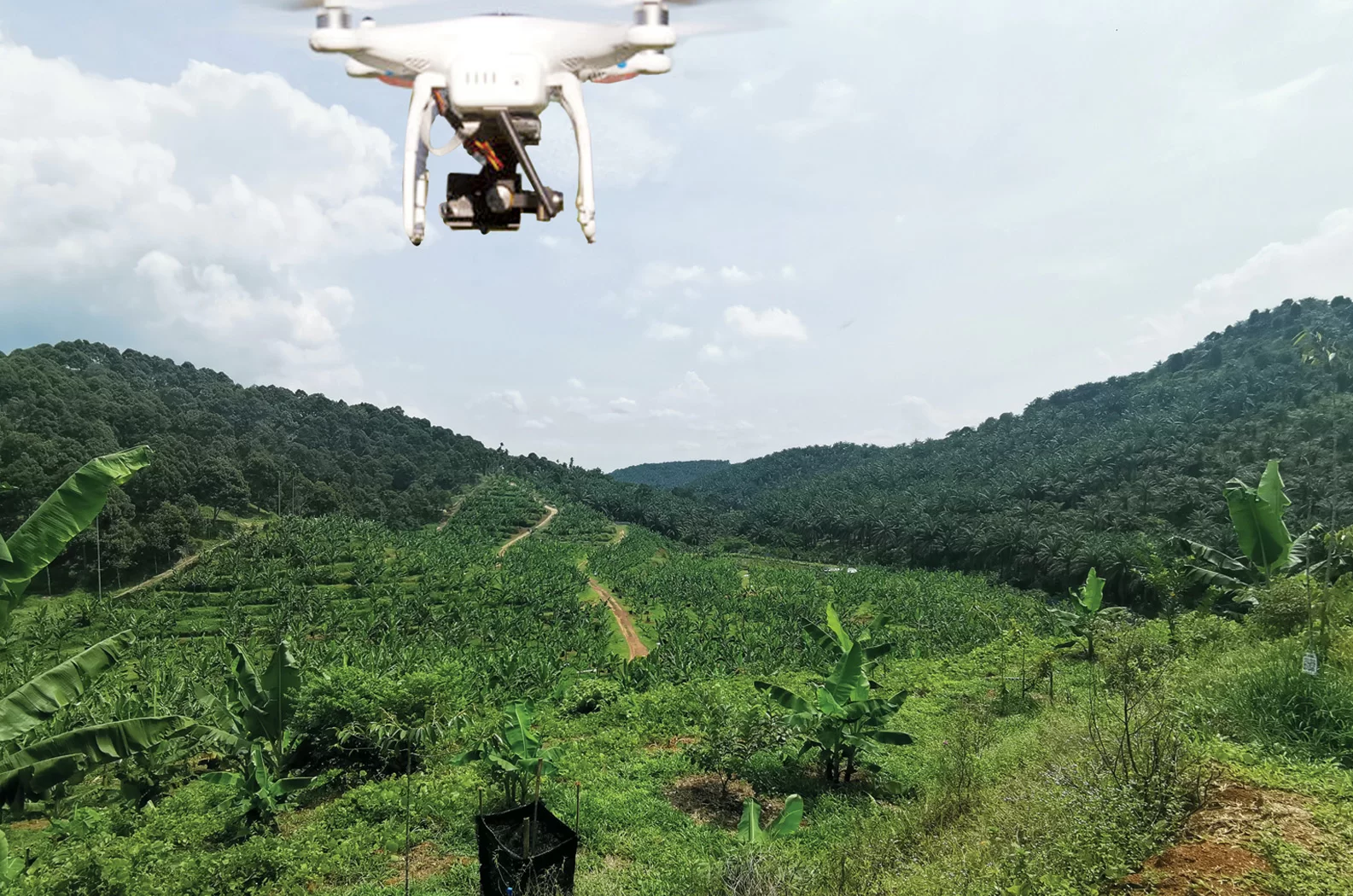

The Use of a UAV or Drone in a Plantation.
3. Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected intelligent devices that communicate and share data over the internet.
Therefore, all devices which are able to access the Internet, such as electronics and agricultural machinery, are said to be part of the IoT.
In durian plantations, IoT technology enables farmers to connect all their agricultural devices and equipment, such as sensors, UAVs, and automatic spraying systems, to a central system.
This allows for real-time monitoring and control of farm operations. Research has found that the IoT technology has assisted farmers in:
- Achieving a higher standard for product quality
- Increasing productivity
- Reducing manual labor
- Optimizing the use of resources
- Improving response to unpredictable situations
The IoT includes features such as the Advanced Irrigation System – which provides regular and optimum daily irrigation, and the Durian Big Data and Smart Recognition System – which allows farmers to monitor the tree’s growth history and overall farm management system.
Interested to discover more about IoT? Learn about Top Fruits’ approach to smart farming here.
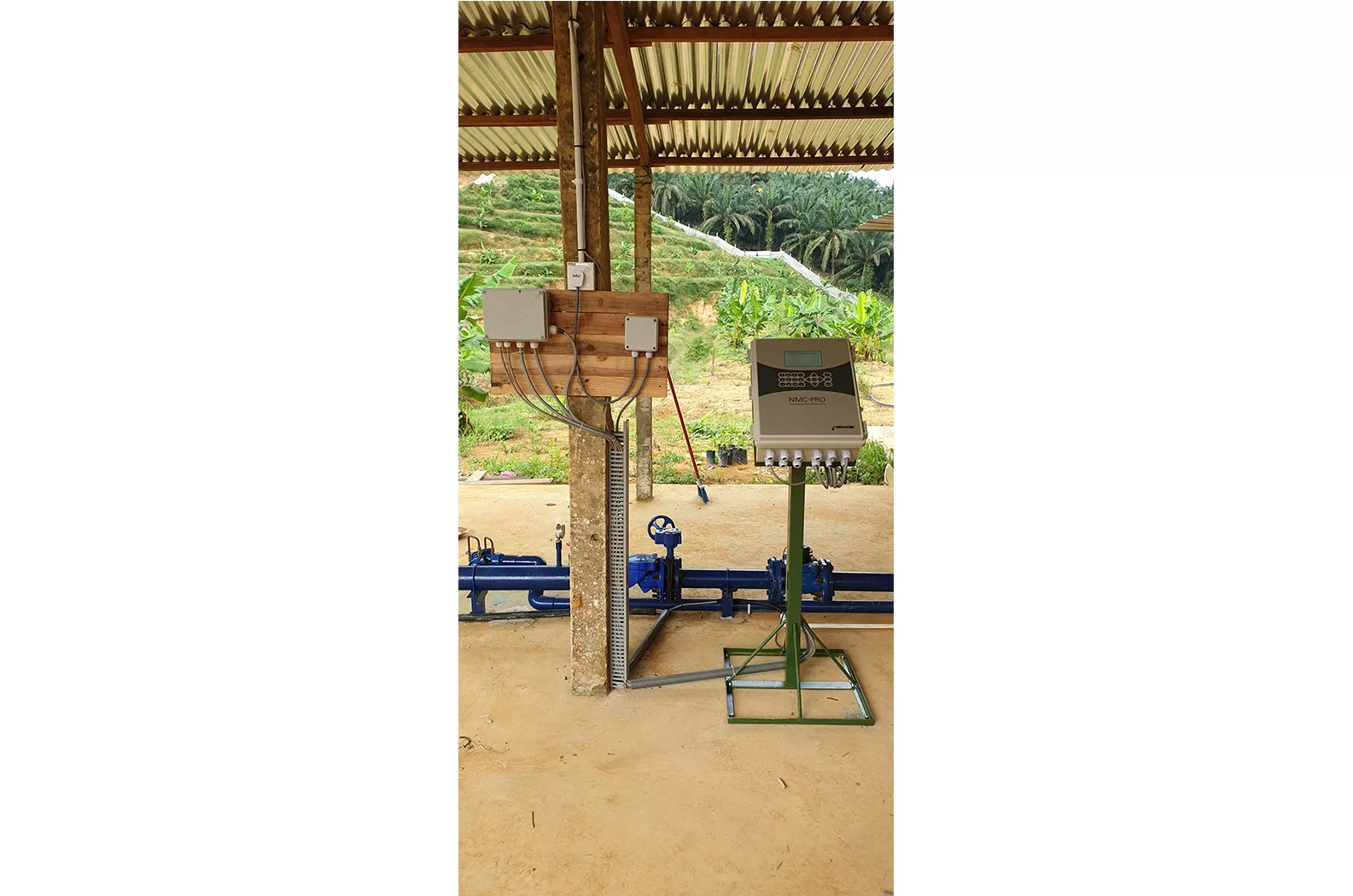

NMC Pro System Manager (Irrigation Management System).
Benefits of Smart Farming to Farmers
In this section, we’ll be discussing the benefits of smart farming to durian farmers:
1. Improvement in Yields
Smart farming technologies offer farmers real-time insights into their plantations, allowing for early detection of potential risks towards durian trees, and enabling precise care for them.
For instance, sensors can track and diagnose durian diseases, monitor weather patterns, evaluate soil fertility, and optimize fertilizer application. Farmers can promptly take action based on this data, or enlist the assistance of autonomous smart management systems.
Therefore, by providing farmers with precise information about the health and needs of their crops, smart farming helps manage resource use, leading to improved yield and reduced destruction of crops.
2. Reduction of Employed Labor
Smart farming technologies streamline agricultural processes, reducing the need for manual labor. This results in lower labor costs, and higher levels of efficiency and precision in durian plantations.
For instance, the use of automatic watering and fertilizer distribution systems. These systems can be remotely activated, reducing the need for labor-intensive tasks and preventing the risk of human errors.
Automated machinery are also able to work longer and more consistent hours, allowing farmers to achieve faster and more efficient results, while conserving resources which can be reinvested towards other critical aspects of farming.
3. Reduction of Operating Costs
By using smart farming technologies, farmers can significantly reduce operating costs associated with labor (as mentioned previously), destruction-related expenses, and resource wastage.
For example, by receiving alerts through SMS, Telegram or email, and activating automated watering systems, farmers can avoid crop losses due to environmental factors such as drought.
Besides, precise application of fertilizers and pesticides minimizes waste and reduces the frequency of applications, leading to significant cost savings in the long run.
Challenges of Smart Farming
Despite the benefits of smart farming strategies, farmers still face many challenges in adopting smart technologies. Here are a few notable ones:
1. Complexity of Technology
The implementation of smart farming requires a good understanding of the smart systems – which are technical knowledge and skills farmers may not possess.
It’s also important to consider that farmers may not have the time and resources to learn how to use these new technologies. This is especially true for farmers who are uneducated.
Therefore, experts have highlighted the government’s role in supporting education and training for farmers, ensuring that they stay updated with the latest agriculture technologies.
Farmers may also reach out and partner with experts experienced in building and implementing smart strategies in durian plantations. This ensures a smooth and guided transition to smart farming.
2. Need for Internet Access
Smart farming requires stable access to the Internet. More specifically, the IoT uses networking protocols such as Internet connectivity, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi.
This proves to be a major issue faced by durian farmers, as most plantations are located in rural areas without high-speed Internet connection.
What’s more, studies recommend the use of the 5G networks in smart applications. This network improves agricultural operations such as:
- Drone control
- Interactive real-time monitoring
- Seeding operations
- Pesticide and fertilizer spraying
- Artificial intelligence robots
The good news is: Most areas in Malaysia, even rural ones, now have Internet access. This improvement can be largely credited to efforts such as the JENDELA project.
This project was a collaboration between the Malaysian Communications and Multimedia Commission (MCMC) and service providers.
Thanks to this project, an estimated 96.92% of populated areas have access to 4G networks as of 31 December 2022. However, efforts are still underway to achieve good Internet connectivity in rural areas.
3. Lack of Standardization
One downside of smart farming is the lack of uniformity in the equipment and software produced by manufacturers.
This means that these machines and devices may not necessarily be compatible with one another.
This problem was highlighted by the International Standardization Organization, where they discussed the need for a unified smart farming system to:
- Ensure a common understanding
- Prevent duplication / overlapping of efforts
- Reduce inefficiencies
Ultimately, the efficiency and productivity brought on by this standardization will result in a cost reduction for farmers and other industry players.
Conclusion
In conclusion, smart farming technology offers great benefits to durian farmers, including improved yields, decreased manual labor, and lower operational costs.
However, navigating the complexities of smart farming demands more than just financial investment – it requires expert guidance.
This is where Top Fruits comes in. We provide comprehensive support to assist you in implementing a robust smart farming system and addressing all your plantation needs.
Explore Smart Farming Solutions With Top Fruits
With more than 30 years in the durian industry, Top Fruits is a leading durian supplier, durian plantation, and durian consultation company Malaysia.
Our team received The Star Export Excellence Awards in 2022 for meeting high standards of quality and authenticity in durian production.
We have supplied durians across Malaysia, to Asian countries such as Hong Kong and China, and are the first Malaysian company to penetrate the African market.
With the goal of helping local durian businesses achieve their full potential, we provide durian consultation services which offer customized solutions and valuable networking opportunities for your durian business.
FAQ
What is smart farming in Malaysia?
Smart farming in Malaysia is the use of advanced technology like sensors and UAVs (drones) to improve agricultural practices, aiming for increased productivity and sustainability.
What is the difference between smart agriculture and smart farming?
Smart agriculture covers the entire agricultural value chain, while smart farming specifically focuses on technology use within farming processes.
What is AI in smart farming?
AI in smart farming involves using advanced algorithms to analyze data and make decisions, like predicting crop yields or detecting pests.
Will AI replace farmers?
No, AI is more likely to assist farmers by providing insights and decision support rather than replacing them entirely.
What are the disadvantages of IoT and AI in agriculture?
Potential drawbacks include technical complexity, access issues in rural areas, and a lack of standardization – making these technologies less accessible or feasible for farmers.
These disadvantages highlight the need for government support, and guidance from industry experts in implementing new technologies.
Learn more on challenges of smart farming here.

